clinical
How effective are body-firming topicals when combined with contouring treatments?
Evaluating the tolerability and efficacy of using a topical body firming moisturiser for pre and post-care of a non-invasive body contouring procedure
Ageing of the skin occurs with time and is due to both natural (intrinsic) and environmental (extrinsic) factors. Intrinsically aged skin is thin and dry, with increased laxity and crepiness, while extrinsically aged skin is thick, coarse, and leathery, with uneven pigmentation.1
Cumulative effects from these ageing processes generate undesirable skin appearance in various body regions, including upper arms, abdomen, buttocks, knees, and thighs. Although exercise can assist in toning and contouring, additional minimally invasive and non-invasive in-office procedures, such as cryolipolysis, radiofrequency, pressure energy, and ultrasound, are often recommended. The demand for these aesthetic procedures for skin tightening and fat reduction increases each year. Nonsurgical fat reduction procedures are up by 135% since 2013.2
Exercise, skin tightening, and fat reduction procedures typically do not address skin quality and skin health; however topical cosmeceuticals may offer a solution. A topical body-firming moisturiser (TBFM), Bodifirm, was created by Revision Skincare to target multiple aspects of aged body skin and to be used as a stand-alone treatment.3 This TBFM was formulated with a patent-pending blend of bioavailable peptides, antioxidants, botanical extracts, and a prebiotic innovation. A randomised, double-blinded, split-body, placebo-controlled stand-alone clinical study illustrated the clinical efficacy of the TBFM in improving laxity, crepiness, and photodamage of the upper arm skin after 12 weeks of twice-daily treatment.3
A clinical case study was designed to assess the efficacy and tolerability of combining the TBFM with a body contouring procedure using simultaneous radiofrequency and targeted energy pressure, pre- and post- treatment, when used twice daily for 17 weeks by women with mild-to-moderate skin laxity, skin crepiness on the knee and upper thigh and mild-to-moderate cellulite on the upper thigh.
METHODS
BTL’s Emtone is an FDA-approved device that simultaneously delivers both thermal and mechanical energy to treat all major contributing factors to cellulite.4 It is clinically proven to increase the density of collagen and elastin, increase dermal thickness, enhance blood supply, and reduce the size of adipocytes.4,6
An open-label, single-centre, randomised, split-body study was carried out. Subjects received four procedures on both the upper thigh and inner thigh with each treatment encompassing 12 minutes of application. The tissue was heated to surface temperatures of 40-45°C which was verified using a built-in infrared thermometer. The initial power setting was set to 70% but was decreased during the treatment depending on the subject’s heat tolerance. Power setting was maintained between 55-70% across all subjects. Procedures were spaced at least one week apart.
Figure 1
Patient Recruitment Criteria: Female subjects, 35-60 years of age, Fitzpatrick Skin Type I-V, BMI between 20-30, with mild-to-moderate skin laxity and skin crepiness on the knee and upper thigh, as well as mild-to-moderate cellulite on the upper thigh, were recruited based on a 10-point Griffiths’ Scale. Subjects were instructed to maintain their lifestyle, maintain weight between +/- 5 lbs from baseline, and avoid the application of any products other than that assigned. All subjects gave written consent and signed a photography release before entering the study.
Patient Protocol: Subjects were randomly assigned to apply the TBFM to one side of their upper and inner thigh and knee consistently twice daily for two weeks before the first Emtone procedure and to continue in between Emtone procedures until the end of the study. Subjects were instructed to use a loofah twice a week to scrub their knee and upper thighs on nonconsecutive days. All patients received Emtone on both knees.
• Clinical Evaluation: Efficacy evaluation for all subjects was performed by two practising dermatologists who were blinded to the assigned TBFM application side of the upper and inner thigh and knee for each subject. An evaluation was performed by reviewing clinical photography at baseline, two weeks TBFM pretreatment, post-first, second, third and fourth procedure, and after one and three months following the fourth procedure using a modified Griffiths’ 10-point scale. (0 = best possible condition, 1-3 = mild, 4-6 =moderate, 7-9 = severe)
• Clinical Photography: Clinical photography using an iPad Pro 11 was taken at baseline, two weeks pre-treatment, post-first procedure, second procedure, third procedure, fourth procedure, after one month and three-month follow-up.
• Self-Assessment Questionnaire: A self-assessment questionnaire was given to subjects at baseline, after two weeks of TBFM pre-treatment, after the fourth Emtone procedure, after one month, and after three-month follow-up from the last procedure. The grading scale is as follows: 5 = completely agree, 4 = somewhat agree, 3 = neither agree/ disagree, 2 = somewhat disagree, 1 = completely disagree.
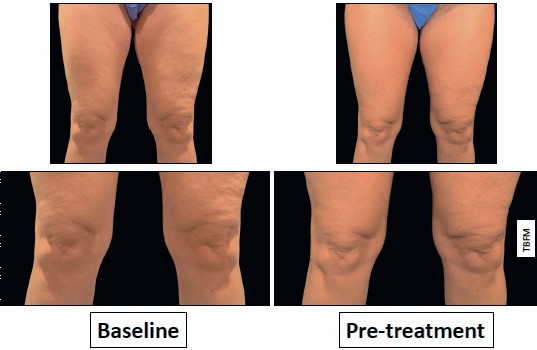
Figure 2: Clinical photography of subject’s upper thighs and knees at baseline, pre treatment,
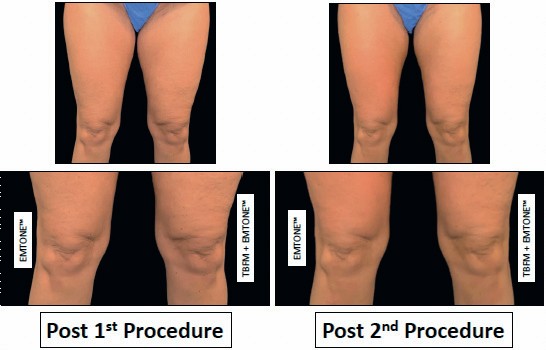
post first procedure,and post second procedure. Subject was 46years oldwith BMI 29.1.
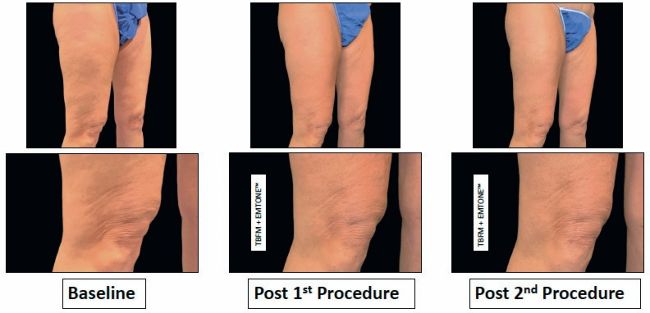
Figure 3: Clinical photography of subject’s upper thighs and knees at baseline, post first procedure, and post second procedure. Subjectwas 54 years oldwith BMI 27.4.
• Cellulite: Statistical significance was achieved (p < 0.01) after the first procedure for both treatment cells. Although at post-first procedure the TBFM and Emtone treated cells had 25% improvement from baseline, this was not a significant improvement (p = 0.0625) but indicative of an improvement.
• Skin Crepiness: In the stand-alone clinical study with the TBFM, statistical significance was observed as early as four weeks in the upper arms.3 In this case study, both treatment cells achieved statistical significance after the second procedure when compared to baseline. A 33% improvement from baseline was calculated for both treatment cells.
• Self-Assessment Questionnaire: AWilcoxon Signed Rank test was performed between baseline and two-week TBFM pre- treatment timepoints. Statistical significance was achieved if p = 0.05. Subjects answered questions within five categories: Firmness/ Tightness, Lines and Skin Texture, Skin Tone, Moisturisation, and Skin Health, specifically focused on the upper thigh and knee treated with the TBFM. The data shows favourable improvement on the thigh and knee after two weeks treated with the TBFM. Statistical significance was not achieved within each category due to the small sample size, n = 5. However, when all the data within each category was combined, the sensitivity increased, and the analysis showed a significant difference between baseline and the two-week TBFM pre-treatment (p < 0.05) for each category.
CONCLUSIONS
• The TBFM was formulated to firm, tighten, and lift sagging, crepey skin to tone and sculpt. In a stand-alone clinical study, the TBFM clinically showed improvement in skin laxity and crepey skin texture after 12 weeks of twice-daily use
• In this case study, subjects perceived an improvement in firmness/ tightness, lines and skin texture, skin tone, moisturisation and skin health on their upper thigh and knee after using the TBFM for two weeks, twice daily before the first procedure
• Clinical photography results are encouraging and demonstrate an improvement in skin sagging, lines, and crepiness on the knee and upper thigh
• This is an ongoing case study
• The results thus far indicate that the TBFM, when applied pre- and post-procedure, may assist in enhancing patient outcomes.
RESULTS
• Tolerability: There were no adverse events reported after two weeks of TBFM pre-treatment and following two Emtone procedures. There was mild erythema immediately after. Emtone procedures, which were resolved.
• Clinical Evaluation: Clinical photography, Figure 2 and Figure 3, was used by two blinded dermatologists to perform their clinical evaluations. The scoring between the two blinded dermatologists was found similar at all time points and treatments. For these reasons, the scores for both dermatologists were combined for the analyses. Statistical analysis was performed (Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test) at each time point and treatment group vs baseline, *p = 0.05 and **p < 0.01. Statistical analysis between treatment cells was not performed.
• Skin Sagging: The two-week TBFM pre-treatment score improved by 25% from baseline and approached statistical significance (p = 0.0625). Upper thigh and knee treated with TBFM and Emtone showed a statistically significant improvement of 25% and 50% from baseline after first and second procedure timepoints, respectively.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors, Alisar Zahr, Thu Nguyen and Tatiana Kononov from Revision Skincare and dermatology consultants Renee Helmick and Anna Paré, would like to thank Dr Michelle Juneau, for clinically grading the subjects in this clinical case study, Fred Wilson for performing the statistical analysis, Ashley Nguyen for providing support in data analysis, Emily Velez in coordination and logistics, and BTL Industries or lending the device.
REFERENCES
1. El-Domyati M, Attia S, Saleh F, et al. Intrinsic ageing vs. photoageing: acomparative histopathological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of skin. Exp Dermatol. 2002;11(5):398- 405.
2. 2018 Statistics. The American Society forAesthetic Plastic Surgery (ASAPS).
3. Kavali, C. M.; Nguyen, T. Q.; Zahr, A. S.; Jiang, L. I.; Kononov, T. (2019).ARandomized, Double-Blind, Split-Body, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Tolerability ofaTopical Body Firming Moisturizer for UpperArm Firming and Rejuvenation. Manuscript submitted for publication.
4. https://bodybybtl.com/solutions/body-contouring/emtone/
5. Fritz, K; Salavastru, C; Gyurova, M. Reduction of abdominal skin laxity in women postvaginal delivery using the synergistic emission of radiofrequency and targeted pressure energies.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018. Oct; 17(5):766-769.
6. Fritz, K; Salavastru, C; Gyurova, M. Clinical evaluation of simultaneously applied monopolar radiofrequency and targeted pressure energy as anew method for noninvasive treatment of cellulite in postpubertal women.JCosmet Dermatol. 2018. Jun; 17(3):361-364.